What Is Trustworthy AI?
Trustworthy AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that are designed and operated in a manner that is ethically sound, safe, transparent, and fair. The concept revolves around ensuring that AI systems are reliable and operate within the bounds of societal and ethical norms. At its core, Trustworthy AI is about building AI technologies that people can rely on and trust.
To achieve Trustworthy AI, several key elements need to be considered. These include ensuring that AI systems are transparent in their operations and decision-making processes, and that they are developed with a focus on fairness to avoid biases. Also, these systems should respect user privacy and data protection norms, and their actions should be accountable and explainable. Additionally, Trustworthy AI should be robust and safe, meaning they should perform reliably under different conditions and be resilient to attacks or errors.
Another important aspect of Trustworthy AI is its adherence to ethical standards. This involves respecting human rights and values, ensuring that AI systems do not cause harm, and that their deployment does not lead to undesirable societal impacts. Ethical AI also means that these systems should be accessible and beneficial to a wide range of users, promoting inclusivity and avoiding discrimination.
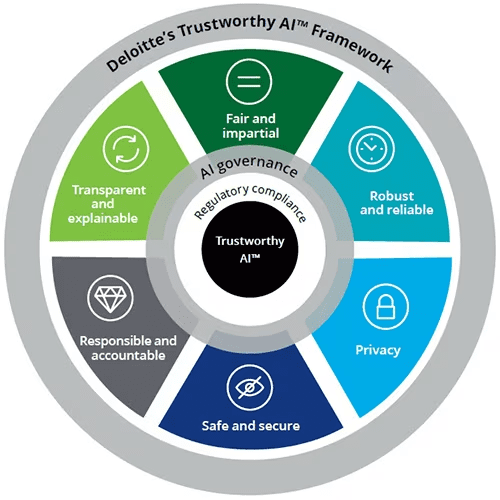
Several government and industry initiatives are underway to provide formal guidelines for trustworthy AI. For example, this image illustrates the Deloitte Trustworthy AI™ Framework.
Some other important trustworthy AI guidelines include:
- European Commission Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI
- US Presidential Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of AI
- NIST research on trustworthy AI
Why We Need Trustworthy AI
Here are a few of the reasons trustworthy AI is becoming a major priority for organizations and governments around the world.
Physical Safety
AI systems are increasingly being used in areas where their decisions can have significant impacts on physical safety. For example, autonomous vehicles rely on AI to make decisions on the road. In healthcare, AI algorithms are used to diagnose diseases and suggest treatments. In both these scenarios, the decisions made by AI can directly impact human lives. Hence, it’s imperative that AI systems are trustworthy and make decisions that are safe and reliable.
We need to trust that the AI will not only perform its tasks efficiently but also not pose any harm. In the event of any unexpected situations, we need to be able to rely on the AI to handle the situation safely. Trustworthy AI, therefore, becomes a necessity to ensure the physical safety of individuals when interacting with or relying on AI systems.
Rights and Liberties
AI systems, particularly those involving data analysis, often have access to vast amounts of personal data. This raises significant concerns about privacy and the potential misuse of this data. Trustworthy AI systems are designed to respect individuals’ rights and liberties, including their right to privacy.
In a world where AI is increasingly being used in decision-making processes, from hiring to loan approvals, there’s a risk of AI systems making decisions that are biased or discriminatory. Trustworthy AI aims to address these concerns by ensuring AI systems are fair and do not infringe on individuals’ rights.
Democracy
AI has the potential to significantly influence democratic processes. For instance, AI can be used to spread misinformation or manipulate public opinion, posing a threat to democratic societies. Trustworthy AI is designed to safeguard our democratic processes by ensuring AI is used responsibly and ethically.
Trustworthy AI can play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of our democratic processes. By ensuring transparency and accountability, trustworthy AI can prevent the misuse of AI for malicious purposes.
7 Ethics Principles for Trustworthy AI
To ensure the development and use of trustworthy AI, several organizations, including the European Commission, have developed ethics guidelines. While there are several approaches to trustworthy AI, and they might use different terminologies, most of them agree on the following basic principles.
1. Human Agency and Oversight
This principle emphasizes that AI systems should empower human beings, allowing them to make informed decisions and fostering their fundamental rights. At the same time, there should be appropriate levels of human oversight over AI systems to ensure their decisions align with our ethical and societal norms.
2. Technical Robustness and Safety
AI systems need to be robust and reliable, and they should behave predictably. This includes ensuring the AI system can handle errors or inconsistencies in the data it processes and can adapt to changing situations. Technical robustness also involves ensuring the security of AI systems and their ability to withstand and recover quickly from attacks or misuse.
3. Privacy and Data Governance
AI systems often process large amounts of data, and it’s critical that this data is handled in a manner that respects individuals’ privacy and complies with data protection laws. This includes ensuring the data used by AI systems is obtained legally and ethically, and that individuals’ privacy is respected throughout the data lifecycle.
4. Transparency
AI systems should be transparent in their decisions and processes, allowing humans to understand how an AI system has reached a particular decision. This includes providing clear and understandable information about the AI system’s capabilities and limitations, and ensuring there is transparency in how the AI system processes data and makes decisions.
5. Accountability
Accountability in AI is about ensuring that individuals and organizations are held responsible for the outcomes of AI systems. It involves clear assignment of responsibility, transparency in decision-making processes, and mechanisms for redress.
This means that if an AI system causes harm or makes a mistake, it should be possible to determine who is responsible. It also means that those affected by the decisions of AI systems should have a means to challenge these decisions.
6. Diversity, Non-Discrimination, and Fairness
Trustworthy AI must uphold principles of diversity, non-discrimination, and fairness. It should respect all humans regardless of their race, gender, age, or other factors. AI systems should be designed and used in a way that respects the rights, diversity, and equality of all individuals.
AI systems should not perpetuate stereotypes or biases. They should be developed using diverse data sets to prevent skewing results or making unjust decisions. AI should provide equal opportunities, and should not create or exacerbate social inequalities.
7. Societal and Environmental Wellbeing
Trustworthy AI should contribute positively to societal and environmental wellbeing. It should be used to solve pressing societal challenges and contribute to the common good. It should respect democracy, the rule of law, and human rights.
AI should also be used responsibly to protect the environment. It should promote sustainable practices and contribute to the fight against climate change. It should not contribute to environmental degradation or the exploitation of natural resources.
Related content: Read our guide to responsible AI
Technological Advances Supporting Trustworthy AI
To implement Trustworthy AI principles, there is a need for technologies and tools that can help make AI more transparent and accountable. Here are a few types of technologies that provide these capabilities.
Explainable AI (XAI)
Explainable AI (XAI) is a critical component of trustworthy AI. XAI refers to AI systems that can provide clear explanations for their decisions and actions. This enables human users to understand, trust, and effectively manage AI.
XAI goes beyond just providing an output or decision. It provides insights into the reasoning behind the decision, making the AI system transparent. With XAI, we can ensure that AI decisions are not a ‘black box’, but are instead clear and understandable.
Bias Detection and Mitigation
Bias in AI can lead to unfair outcomes and discrimination. Therefore, detecting and mitigating bias is crucial for trustworthy AI. This involves identifying potential sources of bias in AI systems and taking steps to minimize their impact. It is important to realize that bias can creep in at various stages of the AI lifecycle, from data collection to model training and deployment.
Bias detection involves identifying biases in data and algorithms. This can be achieved through techniques like statistical analysis, auditing, and testing. Once biases are detected, mitigation strategies can be applied. These can include techniques like data balancing, algorithmic fairness interventions, and robust validation practices
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Systems
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems are a key aspect of trustworthy AI. HITL refers to AI systems where human judgment is integrated into the system’s decision-making process. This ensures that AI does not operate in isolation, but works in collaboration with humans.
HITL systems provide a way to leverage the strengths of both humans and AI. Humans bring their judgment, creativity, and understanding of context, while AI brings its computational power and ability to analyze large amounts of data.
HITL systems also provide a way to ensure accountability and oversight in AI systems. They allow humans to review and override AI decisions if necessary. This promotes transparency, accountability, and trust in AI.
AI Ethics Tools
AI ethics frameworks provide guidelines on ethical considerations in AI development and use. They serve as a roadmap for developers and users to ensure that AI technologies are designed and used responsibly.
An emerging category of AI ethics tools can help operationalize these principles. These can include bias detection tools, privacy-preserving algorithms, and audit tools. These tools enable developers and users to ensure that their AI systems are ethical, fair, and transparent in line with a specific benchmark or guidelines.
Standardization of AI Practices
Standardization of AI practices is essential for trustworthy AI. It involves establishing common standards, metrics, and best practices for the development and use of AI. These standards ensure that all AI systems adhere to a certain level of quality, safety, and ethics.
Standardization can cover various aspects of AI, from data collection and processing to algorithm design and deployment. It can also cover ethical aspects like fairness, privacy, and accountability. The aim of standardization is to create a level playing field where all AI systems meet certain minimum criteria. This ensures consistency, reliability, and trust in AI technologies.
Trustworthy AI with Kolena
Kolena is a machine learning testing and validation platform that solves one of AI’s biggest problems: the lack of trust in model effectiveness. The use cases for AI are enormous, but AI lacks trust from both builders and the public. It is our responsibility to build that trust with full transparency and explainability of ML model performance, not just from a high-level aggregate ‘accuracy’ number, but from rigorous testing and evaluation at scenario levels.
With Kolena, machine learning engineers and data scientists can uncover hidden machine learning model behaviors, easily identify gaps in the test data coverage, and truly learn where and why a model is underperforming, all in minutes, not weeks. Kolena’s AI/ML model testing and validation solution helps developers build safe, reliable, and fair systems by allowing companies to instantly stitch together razor-sharp test cases from their data sets, enabling them to scrutinize AI/ML models in the precise scenarios those models will be unleashed upon the real world. Kolena platform transforms the current nature of AI development from experimental into an engineering discipline that can be trusted and automated.